China launches first commercial ammonia-to-hydrogen refuelling station
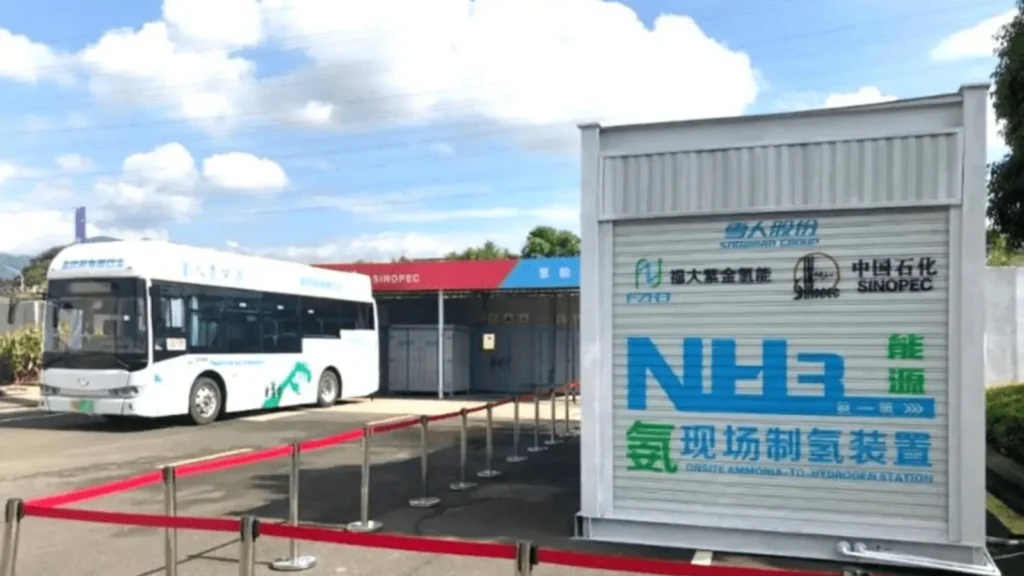

China has inaugurated its first commercial ammonia-to-hydrogen production and refuelling station, marking a major step in hydrogen energy deployment. The new station, located in Nanhai District, Guangdong Province, has a capacity of 1,000 kg of hydrogen per day and is now in full operation, according to Metal.com.
The site is China’s first large-scale commercial facility that integrates ammonia decomposition, hydrogen purification, and refuelling in one closed-loop system. Developed by Fuda Zijin Hydrogen Energy Technology, it represents a shift from demonstration-scale projects to commercial implementation.
Advanced low-temperature ammonia decomposition
Fuda Zijin’s system is based on a low-temperature ammonia decomposition process, operating at approximately 480 °C — a relatively low temperature for ammonia cracking. The process achieves a hydrogen conversion rate of more than 99.5%.
According to the company, its system can cut hydrogen production and transport costs by 40–50% compared with conventional high-pressure delivery, by producing hydrogen on-site from liquid ammonia feedstock.
Unlike traditional refuelling stations, which rely on pre-delivered hydrogen gas, this facility generates hydrogen on demand directly from ammonia. This enables immediate refuelling for vehicles. The station’s 1,000 kg/day output is sufficient to supply more than 100 hydrogen-powered heavy-duty trucks in the region.
Integrated hydrogen production and refuelling
According to Fuda Zijin, its “ammonia-to-hydrogen production on-site” system uses ammonia as a hydrogen energy storage carrier. Integrating hydrogen generation, separation, purification, pressurisation, and refuelling into a single modular platform.
The company states that the system “significantly reduces storage and transportation costs, improves safety, and provides a closed-loop zero-carbon ammonia-hydrogen energy solution.” It can also flexibly adjust production capacity to meet varying hydrogen demand, helping to overcome the “storage and use bottleneck” faced by many refuelling stations.
Fuda Zijin’s technology is being promoted for use across road transport, urban rail transit, and marine applications, offering scalable options for zero-carbon energy infrastructure.
Strengthening Nanhai’s hydrogen hub
The Nanhai District government has positioned itself as a national leader in hydrogen energy development, describing its goal as building the “Capital of China’s Hydrogen Energy Industry.” The new station adds to the area’s growing hydrogen cluster, which includes Huate Gas and Meijin Hydrogen Industrial Headquarters Base.
A milestone for hydrogen logistics
This ammonia-to-hydrogen facility underscores China’s efforts to diversify its hydrogen supply pathways. By combining high efficiency, on-site generation, and cost advantages, the project is expected to accelerate the commercial rollout of fuel-cell trucks and other hydrogen applications in heavy transport.
The use of ammonia as a hydrogen carrier remains a debated but promising approach. It offers clear logistical and cost advantages, especially for heavy transport and long-distance energy storage. However, challenges such as ammonia toxicity, cracking efficiency, and emissions control still require careful management. Industry experts view ammonia not as a replacement for green hydrogen, but as a complementary pathway that can support hydrogen supply and refuelling while broader infrastructure develops.